Ray Marching
一、简介
光线步进,使用shader代码建模,主要的学习资料:Ray Marching and Signed Distance Functions (jamie-wong.com)
如果要应用在Unity中,一般可以用来实现体积云,可参考:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1964y157fA/
另外可以在建模软件中得到模型的SDF,来实现特定形状的体积云,效果可参考:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1LK421i76u/
二、Signed Distance Functions(SDF,有符号距离函数)
构建一个半径为1的球:
代入几个点试试:
第一个点在球面上,第二个点在球内,第三个点在球外
改成代码形式:
float SphereSdf(vec3 p) {
return length(p) - 1.0;
}其他几何形体的SDF可以参考此网站:Inigo Quilez :: computer graphics, mathematics, shaders, fractals, demoscene and more (iquilezles.org)
三、Ray Marching(光线步进)
在Ray Tracing(光线追踪)中,通常定义一个场景里包含有多种几何形体,然后从相机发出视射线(View Ray),根据射线与物体相交情况,计算获取屏幕像素颜色值。光线追踪的原理可以看这个网站:3D Computer Graphics Primer: Ray-Tracing as an Example (scratchapixel.com)
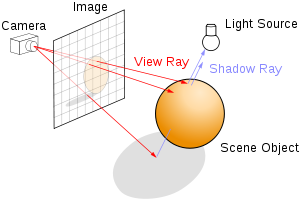
在Ray Marching中,则定义了多个SDF,为了获取射线相交情况,从相机开始发出视射线,逐步前进取点。在逐步前进时不断发出询问:”现在的点是否在场景物体内了?“,相当于:”当前点SDF是否是负数了?“。如果是负数了或者达到最大前进距离了,则结束前进
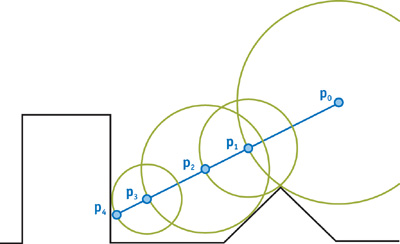
我们可以每次前进一个很小的距离来完成Ray Marching,但是更好的做法是使用Sphere Tracing(球追踪)来完成,可以每次移动更大的安全距离,减少计算量。球追踪算法图示如下
代码形式:
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sceneSDF(eye + depth * viewRayDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
// We're inside the scene surface!
return depth;
}
// Move along the view ray
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
// Gone too far; give up
return end;
}
}
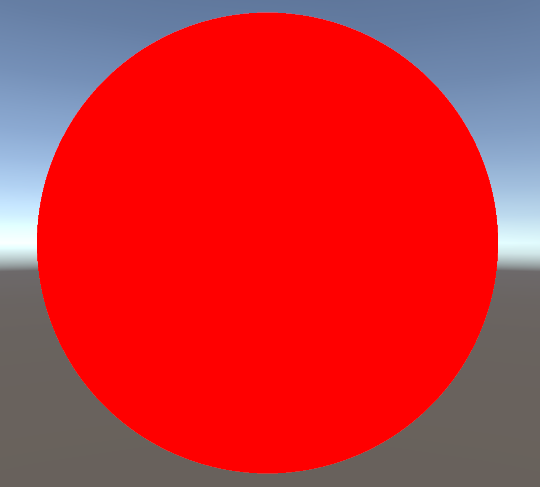
return end;现在用这些理论绘制一个纯红的球:Ray Marching: Part 1 (shadertoy.com)
const int MAX_MARCHING_STEPS = 255; // 最大步进次数
const float MIN_DIST = 0.0; // 最小距离
const float MAX_DIST = 100.0; // 最大距离
const float EPSILON = 0.0001; // 小于此值则可以结束当前步进
// 半径1的球体SDF
float sphereSDF(vec3 samplePoint) {
return length(samplePoint) - 1.0;
}
// 场景SDF
float sceneSDF(vec3 samplePoint) {
return sphereSDF(samplePoint);
}
// 离平面最小距离计算
float shortestDistanceToSurface(vec3 eye, vec3 marchingDirection, float start, float end) {
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sceneSDF(eye + depth * marchingDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
return depth;
}
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
return end;
}
}
return end;
}
// 根据当前片元fragCoord, 计算射线方向
vec3 rayDirection(float fieldOfView, vec2 size, vec2 fragCoord) {
vec2 xy = fragCoord - size / 2.0;
float z = size.y / tan(radians(fieldOfView) / 2.0);
return normalize(vec3(xy, -z));
}
// main
void mainImage(out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord) {
vec3 dir = rayDirection(45.0, iResolution.xy, fragCoord); // 射线方向, fov 45
vec3 eye = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 5.0); // 相机坐标
float dist = shortestDistanceToSurface(eye, dir, MIN_DIST, MAX_DIST);
if (dist > MAX_DIST - EPSILON) {
// Didn't hit anything
fragColor = vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
return;
}
fragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
}
Unity版本,先提供基本框架:
Shader "RayMarching" {
Properties {
_MainTex("Texture", 2D) = "white"{}
}
SubShader {
Tags {
"Queue" = "Transparent"
"RenderType" = "Transparent"
}
Lighting Off
ZWrite Off
Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
v2f vert(appdata v) {
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
UNITY_TRANSFER_FOG(o,o.vertex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target {
return 0;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}然后补上Ray Marching算法:
Shader "RayMarching" {
Properties {
_MainTex("Texture", 2D) = "white"{}
}
SubShader {
Tags {
"Queue" = "Transparent"
"RenderType" = "Transparent"
}
Lighting Off
ZWrite Off
Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
v2f vert(appdata v) {
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
UNITY_TRANSFER_FOG(o,o.vertex);
return o;
}
#define MAX_MARCHING_STEPS 255
#define MIN_DIST 0
#define MAX_DIST 100
#define EPSILON 0.0001
float sphereSDF(float3 samplePoint) {
return length(samplePoint) - 1;
}
float sceneSDF(float3 samplePoint) {
return sphereSDF(samplePoint);
}
float shortestDistanceToSurface(float3 eye, float3 marchingDirection, float start, float end) {
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sceneSDF(eye + depth * marchingDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
return depth;
}
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
return end;
}
}
return end;
}
float3 rayDirection(float fieldOfView, float2 size, float2 fragCoord) {
float2 xy = fragCoord - size * 0.5;
float z = size.y / tan(radians(fieldOfView) * 0.5);
return normalize(float3(xy, -z));
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target {
float3 dir = rayDirection(45, 1, i.uv); // 参数size用1x1就行
float3 eye = float3(0, 0, 5);
float dist = shortestDistanceToSurface(eye, dir, MIN_DIST, MAX_DIST);
if (dist > MAX_DIST - EPSILON) {
return 0;
}
return fixed4(1, 0, 0, 1);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}创建材质,拖到平面物体上,得到的效果:

四、平面法线与光照
法线相当于计算SDF的梯度,公式:
但是不需要一定用微积分来获得精确结果,可以使用这样的形式获取法线:
对应的代码为:
vec3 estimateNormal(vec3 p) {
return normalize(vec3(
sceneSDF(vec3(p.x + EPSILON, p.y, p.z)) - sceneSDF(vec3(p.x - EPSILON, p.y, p.z)),
sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y + EPSILON, p.z)) - sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y - EPSILON, p.z)),
sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y, p.z + EPSILON)) - sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y, p.z - EPSILON))
));
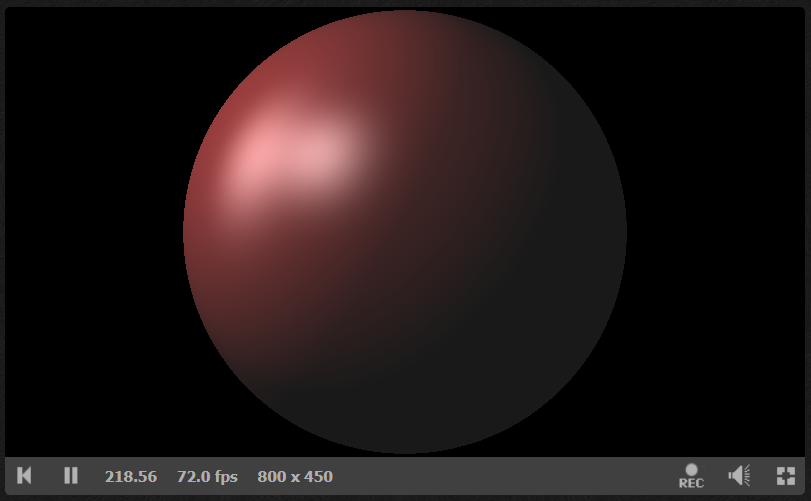
}有了法线计算公式后可以应用上Phong光照模型,完整代码:Ray Marching: Part 2 (shadertoy.com)
const int MAX_MARCHING_STEPS = 255;
const float MIN_DIST = 0.0;
const float MAX_DIST = 100.0;
const float EPSILON = 0.0001;
float sphereSDF(vec3 samplePoint) {
return length(samplePoint) - 1.0;
}
float sceneSDF(vec3 samplePoint) {
return sphereSDF(samplePoint);
}
float shortestDistanceToSurface(vec3 eye, vec3 marchingDirection, float start, float end) {
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sceneSDF(eye + depth * marchingDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
return depth;
}
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
return end;
}
}
return end;
}
vec3 rayDirection(float fieldOfView, vec2 size, vec2 fragCoord) {
vec2 xy = fragCoord - size / 2.0;
float z = size.y / tan(radians(fieldOfView) / 2.0);
return normalize(vec3(xy, -z));
}
vec3 estimateNormal(vec3 p) {
return normalize(vec3(
sceneSDF(vec3(p.x + EPSILON, p.y, p.z)) - sceneSDF(vec3(p.x - EPSILON, p.y, p.z)),
sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y + EPSILON, p.z)) - sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y - EPSILON, p.z)),
sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y, p.z + EPSILON)) - sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y, p.z - EPSILON))
));
}
// Phong光照模型
/**
* Lighting contribution of a single point light source via Phong illumination.
*
* The vec3 returned is the RGB color of the light's contribution.
*
* k_a: Ambient color
* k_d: Diffuse color
* k_s: Specular color
* alpha: Shininess coefficient
* p: position of point being lit
* eye: the position of the camera
* lightPos: the position of the light
* lightIntensity: color/intensity of the light
*
* See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phong_reflection_model#Description
*/
vec3 phongContribForLight(vec3 k_d, vec3 k_s, float alpha, vec3 p, vec3 eye, vec3 lightPos, vec3 lightIntensity) {
vec3 N = estimateNormal(p);
vec3 L = normalize(lightPos - p);
vec3 V = normalize(eye - p);
vec3 R = normalize(reflect(-L, N));
float dotLN = dot(L, N);
float dotRV = dot(R, V);
if (dotLN < 0.0) {
// Light not visible from this point on the surface
return vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
if (dotRV < 0.0) {
// Light reflection in opposite direction as viewer, apply only diffuse
// component
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN);
}
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN + k_s * pow(dotRV, alpha));
}
// 添加多个光照
/**
* Lighting via Phong illumination.
*
* The vec3 returned is the RGB color of that point after lighting is applied.
* k_a: Ambient color
* k_d: Diffuse color
* k_s: Specular color
* alpha: Shininess coefficient
* p: position of point being lit
* eye: the position of the camera
*
* See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phong_reflection_model#Description
*/
vec3 phongIllumination(vec3 k_a, vec3 k_d, vec3 k_s, float alpha, vec3 p, vec3 eye) {
const vec3 ambientLight = 0.5 * vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
vec3 color = ambientLight * k_a;
vec3 light1Pos = vec3(4.0 * sin(iTime),
2.0,
4.0 * cos(iTime));
vec3 light1Intensity = vec3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye,
light1Pos,
light1Intensity);
vec3 light2Pos = vec3(2.0 * sin(0.37 * iTime),
2.0 * cos(0.37 * iTime),
2.0);
vec3 light2Intensity = vec3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye,
light2Pos,
light2Intensity);
return color;
}
void mainImage(out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord) {
vec3 dir = rayDirection(45.0, iResolution.xy, fragCoord);
vec3 eye = vec3(0.0, 0.0, 5.0);
float dist = shortestDistanceToSurface(eye, dir, MIN_DIST, MAX_DIST);
if (dist > MAX_DIST - EPSILON) {
// Didn't hit anything
fragColor = vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
return;
}
// The closest point on the surface to the eyepoint along the view ray
vec3 p = eye + dist * dir;
vec3 K_a = vec3(0.2, 0.2, 0.2);
vec3 K_d = vec3(0.7, 0.2, 0.2);
vec3 K_s = vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
float shininess = 10.0;
vec3 color = phongIllumination(K_a, K_d, K_s, shininess, p, eye);
fragColor = vec4(color, 1.0);
}
同样的提供一个Unity版本:
Shader "RayMarching" {
Properties {
_MainTex("Texture", 2D) = "white"{}
}
SubShader {
Tags {
"Queue" = "Transparent"
"RenderType" = "Transparent"
}
Lighting Off
ZWrite Off
Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
v2f vert(appdata v) {
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
UNITY_TRANSFER_FOG(o,o.vertex);
return o;
}
#define MAX_MARCHING_STEPS 255
#define MIN_DIST 0
#define MAX_DIST 100
#define EPSILON 0.0001
float sphereSDF(float3 samplePoint) {
return length(samplePoint) - 1;
}
float sceneSDF(float3 samplePoint) {
return sphereSDF(samplePoint);
}
float shortestDistanceToSurface(float3 eye, float3 marchingDirection, float start, float end) {
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sceneSDF(eye + depth * marchingDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
return depth;
}
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
return end;
}
}
return end;
}
float3 rayDirection(float fieldOfView, float2 size, float2 fragCoord) {
float2 xy = fragCoord - size * 0.5;
float z = size.y / tan(radians(fieldOfView) * 0.5);
return normalize(float3(xy, -z));
}
float3 estimateNormal(float3 p) {
return normalize(float3(
sceneSDF(float3(p.x + EPSILON, p.y, p.z)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x - EPSILON, p.y, p.z)),
sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y + EPSILON, p.z)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y - EPSILON, p.z)),
sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z + EPSILON)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z - EPSILON))
));
}
float3 phongContribForLight(float3 k_d, float3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye, float3 lightPos, float3 lightIntensity) {
float3 N = estimateNormal(p);
float3 L = normalize(lightPos - p);
float3 V = normalize(eye - p);
float3 R = normalize(reflect(-L, N));
float dotLN = dot(L, N);
float dotRV = dot(R, V);
if (dotLN < 0.0) {
// Light not visible from this point on the surface
return float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
if (dotRV < 0.0) {
// Light reflection in opposite direction as viewer, apply only diffuse
// component
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN);
}
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN + k_s * pow(dotRV, alpha));
}
float3 phongIllumination(float3 k_a, float3 k_d, float3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye) {
float iTime = _Time.y;
const float3 ambientLight = 0.5 * float3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
float3 color = ambientLight * k_a;
float3 light1Pos = float3(4.0 * sin(iTime), 2.0, 4.0 * cos(iTime));
float3 light1Intensity = float3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye, light1Pos, light1Intensity);
float3 light2Pos = float3(2.0 * sin(0.37 * iTime), 2.0 * cos(0.37 * iTime), 2.0);
float3 light2Intensity = float3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye, light2Pos, light2Intensity);
return color;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target {
float3 dir = rayDirection(45, 1, i.uv);
float3 eye = float3(0, 0, 5);
float dist = shortestDistanceToSurface(eye, dir, MIN_DIST, MAX_DIST);
if (dist > MAX_DIST - EPSILON) {
return 0;
}
// The closest point on the surface to the eyepoint along the view ray
float3 p = eye + dist * dir;
float3 K_a = 0.03;
float3 K_d = float3(0.7, 0.2, 0.2);
float3 K_s = 1;
float shininess = 10.0;
float3 color = phongIllumination(K_a, K_d, K_s, shininess, p, eye);
return fixed4(color, 1);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}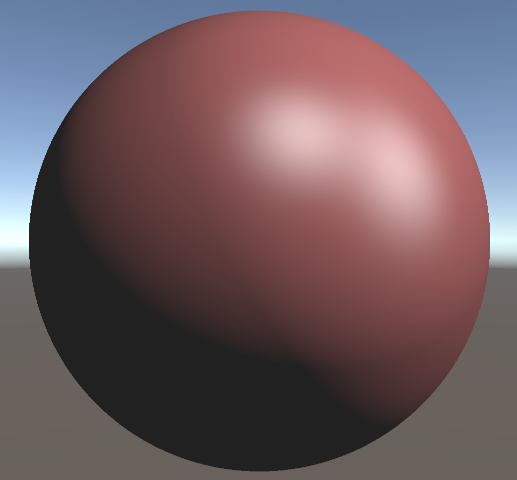
五、相机移动
可以以OpenGL中的gluLookAt函数为参考,来写自己的相机矩阵来控制相机移动:
/**
* Return a transformation matrix that will transform a ray from view space
* to world coordinates, given the eye point, the camera target, and an up vector.
*
* This assumes that the center of the camera is aligned with the negative z axis in
* view space when calculating the ray marching direction.
*/
mat4 viewMatrix(vec3 eye, vec3 center, vec3 up) {
vec3 f = normalize(center - eye);
vec3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
vec3 u = cross(s, f);
return mat4(
vec4(s, 0.0),
vec4(u, 0.0),
vec4(-f, 0.0),
vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1)
);
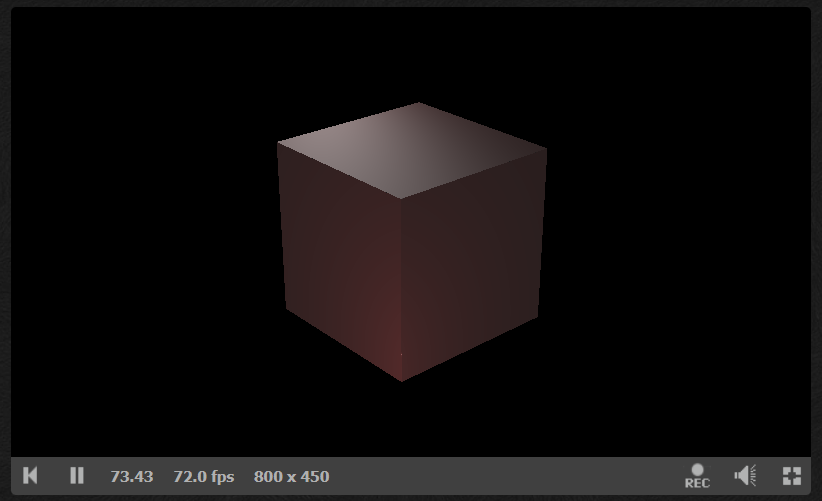
}示例,让相机在(8, 5, 7)这个坐标正面看着一个矩形:
const int MAX_MARCHING_STEPS = 255;
const float MIN_DIST = 0.0;
const float MAX_DIST = 100.0;
const float EPSILON = 0.0001;
float cubeSDF(vec3 p) {
vec3 d = abs(p) - vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
float insideDistance = min(max(d.x, max(d.y, d.z)), 0.0);
float outsideDistance = length(max(d, 0.0));
return insideDistance + outsideDistance;
}
float sceneSDF(vec3 samplePoint) {
return cubeSDF(samplePoint);
}
float shortestDistanceToSurface(vec3 eye, vec3 marchingDirection, float start, float end) {
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sceneSDF(eye + depth * marchingDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
return depth;
}
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
return end;
}
}
return end;
}
vec3 rayDirection(float fieldOfView, vec2 size, vec2 fragCoord) {
vec2 xy = fragCoord - size / 2.0;
float z = size.y / tan(radians(fieldOfView) / 2.0);
return normalize(vec3(xy, -z));
}
vec3 estimateNormal(vec3 p) {
return normalize(vec3(
sceneSDF(vec3(p.x + EPSILON, p.y, p.z)) - sceneSDF(vec3(p.x - EPSILON, p.y, p.z)),
sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y + EPSILON, p.z)) - sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y - EPSILON, p.z)),
sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y, p.z + EPSILON)) - sceneSDF(vec3(p.x, p.y, p.z - EPSILON))
));
}
vec3 phongContribForLight(vec3 k_d, vec3 k_s, float alpha, vec3 p, vec3 eye, vec3 lightPos, vec3 lightIntensity) {
vec3 N = estimateNormal(p);
vec3 L = normalize(lightPos - p);
vec3 V = normalize(eye - p);
vec3 R = normalize(reflect(-L, N));
float dotLN = dot(L, N);
float dotRV = dot(R, V);
if (dotLN < 0.0) {
// Light not visible from this point on the surface
return vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
if (dotRV < 0.0) {
// Light reflection in opposite direction as viewer, apply only diffuse
// component
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN);
}
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN + k_s * pow(dotRV, alpha));
}
vec3 phongIllumination(vec3 k_a, vec3 k_d, vec3 k_s, float alpha, vec3 p, vec3 eye) {
const vec3 ambientLight = 0.5 * vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
vec3 color = ambientLight * k_a;
vec3 light1Pos = vec3(4.0 * sin(iTime),
2.0,
4.0 * cos(iTime));
vec3 light1Intensity = vec3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye,
light1Pos,
light1Intensity);
vec3 light2Pos = vec3(2.0 * sin(0.37 * iTime),
2.0 * cos(0.37 * iTime),
2.0);
vec3 light2Intensity = vec3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye,
light2Pos,
light2Intensity);
return color;
}
mat4 viewMatrix(vec3 eye, vec3 center, vec3 up) {
// Based on gluLookAt man page
vec3 f = normalize(center - eye);
vec3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
vec3 u = cross(s, f);
return mat4(
vec4(s, 0.0),
vec4(u, 0.0),
vec4(-f, 0.0),
vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1)
);
}
void mainImage(out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord) {
vec3 viewDir = rayDirection(45.0, iResolution.xy, fragCoord);
vec3 eye = vec3(8.0, 5.0, 7.0);
mat4 viewToWorld = viewMatrix(eye, vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0));
vec3 worldDir = (viewToWorld * vec4(viewDir, 0.0)).xyz;
float dist = shortestDistanceToSurface(eye, worldDir, MIN_DIST, MAX_DIST);
if (dist > MAX_DIST - EPSILON) {
// Didn't hit anything
fragColor = vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
return;
}
// The closest point on the surface to the eyepoint along the view ray
vec3 p = eye + dist * worldDir;
vec3 K_a = vec3(0.2, 0.2, 0.2);
vec3 K_d = vec3(0.7, 0.2, 0.2);
vec3 K_s = vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
float shininess = 10.0;
vec3 color = phongIllumination(K_a, K_d, K_s, shininess, p, eye);
fragColor = vec4(color, 1.0);
}
Unity版本:
Shader "RayMarching" {
Properties {
_MainTex("Texture", 2D) = "white"{}
}
SubShader {
Tags {
"Queue" = "Transparent"
"RenderType" = "Transparent"
}
Lighting Off
ZWrite Off
Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
v2f vert(appdata v) {
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
UNITY_TRANSFER_FOG(o,o.vertex);
return o;
}
#define MAX_MARCHING_STEPS 255
#define MIN_DIST 0
#define MAX_DIST 100
#define EPSILON 0.0001
float cubeSDF(float3 p) {
float3 d = abs(p) - 1;
float insideDistance = min(max(d.x, max(d.y, d.z)), 0);
float outsideDistance = length(max(d, 0));
return insideDistance + outsideDistance;
}
float sceneSDF(float3 samplePoint) {
return cubeSDF(samplePoint);
}
float shortestDistanceToSurface(float3 eye, float3 marchingDirection, float start, float end) {
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sceneSDF(eye + depth * marchingDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
return depth;
}
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
return end;
}
}
return end;
}
float3 rayDirection(float fieldOfView, float2 size, float2 fragCoord) {
float2 xy = fragCoord - size * 0.5;
float z = size.y / tan(radians(fieldOfView) * 0.5);
return normalize(float3(xy, -z));
}
float3 estimateNormal(float3 p) {
return normalize(float3(
sceneSDF(float3(p.x + EPSILON, p.y, p.z)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x - EPSILON, p.y, p.z)),
sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y + EPSILON, p.z)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y - EPSILON, p.z)),
sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z + EPSILON)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z - EPSILON))
));
}
float3 phongContribForLight(float3 k_d, float3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye, float3 lightPos, float3 lightIntensity) {
float3 N = estimateNormal(p);
float3 L = normalize(lightPos - p);
float3 V = normalize(eye - p);
float3 R = normalize(reflect(-L, N));
float dotLN = dot(L, N);
float dotRV = dot(R, V);
if (dotLN < 0.0) {
// Light not visible from this point on the surface
return float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
if (dotRV < 0.0) {
// Light reflection in opposite direction as viewer, apply only diffuse
// component
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN);
}
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN + k_s * pow(dotRV, alpha));
}
float3 phongIllumination(float3 k_a, float3 k_d, float3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye) {
float iTime = _Time.y;
const float3 ambientLight = 0.5 * float3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
float3 color = ambientLight * k_a;
float3 light1Pos = float3(4.0 * sin(iTime), 2.0, 4.0 * cos(iTime));
float3 light1Intensity = float3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye, light1Pos, light1Intensity);
float3 light2Pos = float3(2.0 * sin(0.37 * iTime), 2.0 * cos(0.37 * iTime), 2.0);
float3 light2Intensity = float3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye, light2Pos, light2Intensity);
return color;
}
float4x4 viewMatrix(float3 eye, float3 center, float3 up) {
// Based on gluLookAt man page
float3 f = normalize(center - eye);
float3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
float3 u = cross(s, f);
return float4x4(
float4(s, 0),
float4(u, 0),
float4(-f, 0),
float4(0, 0, 0, 1)
);
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target {
float3 viewDir = rayDirection(45, 1, i.uv);
float3 eye = float3(8, 5, 7);
float4x4 viewToWorld = viewMatrix(eye, 0, float3(0, 1, 0));
float3 worldDir = mul(float4(viewDir, 0), viewToWorld).xyz; // 这里需要反过来使用mul计算
float dist = shortestDistanceToSurface(eye, worldDir, MIN_DIST, MAX_DIST);
if (dist > MAX_DIST - EPSILON) {
// Didn't hit anything
return 0;
}
// The closest point on the surface to the eyepoint along the view ray
float3 p = eye + dist * worldDir;
float3 K_a = 0.03;
float3 K_d = float3(0.7, 0.2, 0.2);
float3 K_s = 1;
float shininess = 10.0;
float3 color = phongIllumination(K_a, K_d, K_s, shininess, p, eye);
return fixed4(color, 1);
}
ENDCG
}
}
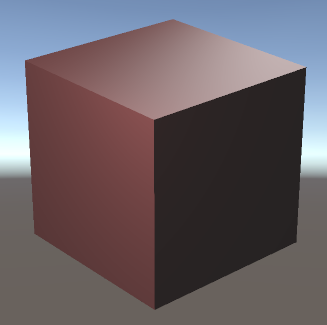
}
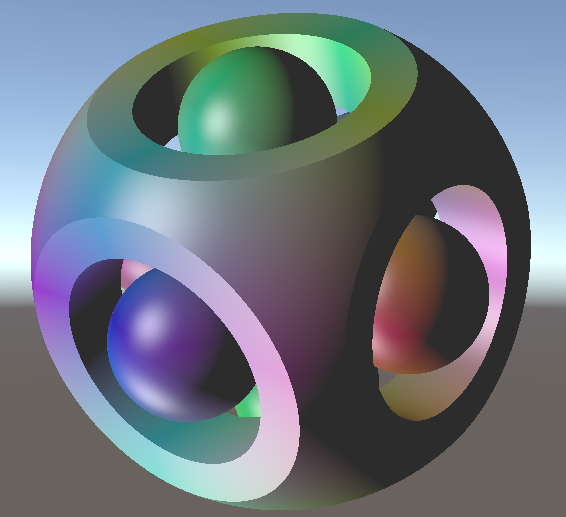
六、构建几何体
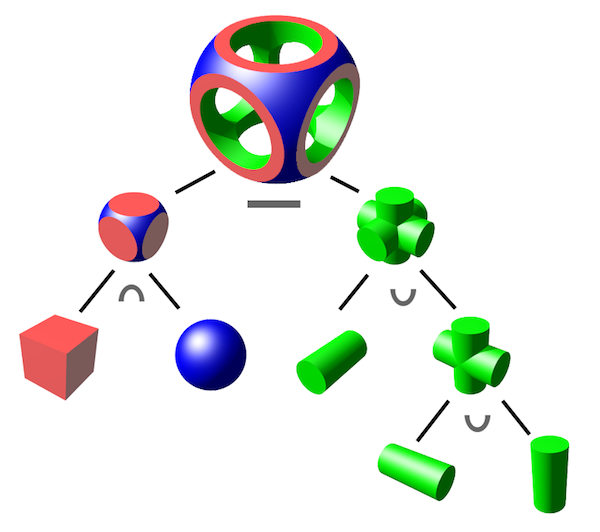
需要使用三种基础运算符:
- ∩:intersection,相交
- ∪:union,组合
- −:difference,差异
对应的代码为:
float intersectSDF(float distA, float distB) {
return max(distA, distB);
}
float unionSDF(float distA, float distB) {
return min(distA, distB);
}
float differenceSDF(float distA, float distB) {
return max(distA, -distB);
}其中负的SDF相当于内外翻转的几何体,所以函数differenceSDF做的就是A几何体和内外翻转的B几何体相交的结果
另外还有别的其他构建几何体的运算,可以参考此网站的Primitive combinations部分:Inigo Quilez :: computer graphics, mathematics, shaders, fractals, demoscene and more (iquilezles.org)
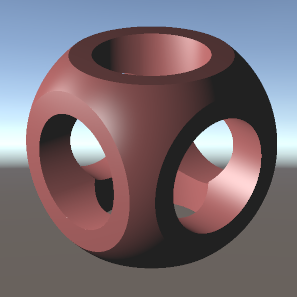
Unity构建上图的结果:
Shader "RayMarching" {
Properties {
_MainTex("Texture", 2D) = "white"{}
}
SubShader {
Tags {
"Queue" = "Transparent"
"RenderType" = "Transparent"
}
Lighting Off
ZWrite Off
Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
v2f vert(appdata v) {
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
UNITY_TRANSFER_FOG(o,o.vertex);
return o;
}
#define MAX_MARCHING_STEPS 255
#define MIN_DIST 0
#define MAX_DIST 100
#define EPSILON 0.0001
float sphereSDF(float3 p, float r) {
return length(p) - r;
}
float cubeSDF(float3 p, float w) {
float3 d = abs(p) - w;
float insideDistance = min(max(d.x, max(d.y, d.z)), 0);
float outsideDistance = length(max(d, 0));
return insideDistance + outsideDistance;
}
float cylinderSDF(float3 p, float h, float r) {
float2 d = abs(float2(length(p.xz), p.y)) - float2(r, h);
return min(max(d.x, d.y), 0) + length(max(d, 0));
}
float sceneSDF(float3 p) {
float cube = cubeSDF(p, 1);
float sphere = sphereSDF(p, 1.3);
float cylinderA = cylinderSDF(p, 2, 0.6); // 圆柱体稍微长一些, 需要挖穿几何体
float cylinderB = cylinderSDF(float3(p.y, p.x, p.z), 2, 0.6);
float cylinderC = cylinderSDF(float3(p.x, p.z, p.y), 2, 0.6);
return max(max(cube, sphere), -min(min(cylinderA, cylinderB), cylinderC));
}
float shortestDistanceToSurface(float3 eye, float3 marchingDirection, float start, float end) {
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sceneSDF(eye + depth * marchingDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
return depth;
}
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
return end;
}
}
return end;
}
float3 rayDirection(float fieldOfView, float2 size, float2 fragCoord) {
float2 xy = fragCoord - size * 0.5;
float z = size.y / tan(radians(fieldOfView) * 0.5);
return normalize(float3(xy, -z));
}
float3 estimateNormal(float3 p) {
return normalize(float3(
sceneSDF(float3(p.x + EPSILON, p.y, p.z)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x - EPSILON, p.y, p.z)),
sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y + EPSILON, p.z)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y - EPSILON, p.z)),
sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z + EPSILON)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z - EPSILON))
));
}
float3 phongContribForLight(float3 k_d, float3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye, float3 lightPos, float3 lightIntensity) {
float3 N = estimateNormal(p);
float3 L = normalize(lightPos - p);
float3 V = normalize(eye - p);
float3 R = normalize(reflect(-L, N));
float dotLN = dot(L, N);
float dotRV = dot(R, V);
if (dotLN < 0.0) {
// Light not visible from this point on the surface
return float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
if (dotRV < 0.0) {
// Light reflection in opposite direction as viewer, apply only diffuse
// component
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN);
}
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN + k_s * pow(dotRV, alpha));
}
float3 phongIllumination(float3 k_a, float3 k_d, float3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye) {
float iTime = _Time.y;
const float3 ambientLight = 0.5 * float3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
float3 color = ambientLight * k_a;
float3 light1Pos = float3(4.0 * sin(iTime), 2.0, 4.0 * cos(iTime));
float3 light1Intensity = float3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye, light1Pos, light1Intensity);
float3 light2Pos = float3(2.0 * sin(0.37 * iTime), 2.0 * cos(0.37 * iTime), 2.0);
float3 light2Intensity = float3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye, light2Pos, light2Intensity);
return color;
}
float4x4 viewMatrix(float3 eye, float3 center, float3 up) {
// Based on gluLookAt man page
float3 f = normalize(center - eye);
float3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
float3 u = cross(s, f);
return float4x4(
float4(s, 0),
float4(u, 0),
float4(-f, 0),
float4(0, 0, 0, 1)
);
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target {
float3 viewDir = rayDirection(45, 1, i.uv);
float3 eye = float3(8, 5, 7);
float4x4 viewToWorld = viewMatrix(eye, 0, float3(0, 1, 0));
float3 worldDir = mul(float4(viewDir, 0), viewToWorld).xyz; // 这里需要反过来使用mul计算
float dist = shortestDistanceToSurface(eye, worldDir, MIN_DIST, MAX_DIST);
if (dist > MAX_DIST - EPSILON) {
// Didn't hit anything
return 0;
}
// The closest point on the surface to the eyepoint along the view ray
float3 p = eye + dist * worldDir;
float3 K_a = 0.03;
float3 K_d = float3(0.7, 0.2, 0.2);
float3 K_s = 1;
float shininess = 10.0;
float3 color = phongIllumination(K_a, K_d, K_s, shininess, p, eye);
return fixed4(color, 1);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
七、模型变换
7.1 位移和旋转
位移只需要控制采样点偏移就行:
float sceneSDF(vec3 samplePoint) {
float sphereDist = sphereSDF(samplePoint / 1.2) * 1.2;
float cubeDist = cubeSDF(samplePoint + vec3(0.0, sin(iGlobalTime), 0.0));
return intersectSDF(cubeDist, sphereDist);
}旋转则使用旋转矩阵乘上采样点的方式:
mat4 rotateY(float theta) {
float c = cos(theta);
float s = sin(theta);
return mat4(
vec4(c, 0, s, 0),
vec4(0, 1, 0, 0),
vec4(-s, 0, c, 0),
vec4(0, 0, 0, 1)
);
}
float sceneSDF(vec3 samplePoint) {
float sphereDist = sphereSDF(samplePoint / 1.2) * 1.2;
vec3 cubePoint = (invert(rotateY(iGlobalTime)) * vec4(samplePoint, 1.0)).xyz;
float cubeDist = cubeSDF(cubePoint);
return intersectSDF(cubeDist, sphereDist);
}7.2 均匀缩放
均匀缩放则需要采样点先除以缩放值,再把SDF结果乘上缩放值:
float dist = someSDF(samplePoint / scalingFactor) * scalingFactor;原因是对采样点进行整体缩放x倍后,SDF得到的结果也会被整体缩放x倍,因此需要将SDF的结果乘上x来补偿这个差异。如果不对这个SDF的结果进行补偿,则可能会影响Ray Marching步进算法中的Sphere Tracing算法的步进距离估算,导致可能步进距离过长没有渲染出来图像
例如半径为1的球体的SDF是:
假如整体缩放50%,则变成半径为0.5的球体:
并提供一个错误的未对缩放补偿的版本:
代入SDF为0、1的点和原点试试:
可以发现函数g的SDF结果是拥有正确的距离计算的,而未补偿的函数h的SDF结果则没有正确的距离计算(例如原点与半径为0.5的球体表面距离应该是-0.5,而不是-1)
7.3 非均匀缩放
非均匀缩放需要避免步进距离过长导致渲染错误,因此需要这样补偿:
float dist = someSDF(samplePoint / vec3(s_x, s_y, s_z)) * min(s_x, min(s_y, s_z));八、最终合并在一起
Shader "RayMarching" {
Properties {
_MainTex("Texture", 2D) = "white"{}
}
SubShader {
Tags {
"Queue" = "Transparent"
"RenderType" = "Transparent"
}
Lighting Off
ZWrite Off
Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata {
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f {
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
v2f vert(appdata v) {
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
UNITY_TRANSFER_FOG(o,o.vertex);
return o;
}
#define MAX_MARCHING_STEPS 255
#define MIN_DIST 0
#define MAX_DIST 100
#define EPSILON 0.0001
float sphereSDF(float3 p, float r) {
return length(p) - r;
}
float cubeSDF(float3 p, float w) {
float3 d = abs(p) - w;
float insideDistance = min(max(d.x, max(d.y, d.z)), 0);
float outsideDistance = length(max(d, 0));
return insideDistance + outsideDistance;
}
float cylinderSDF(float3 p, float h, float r) {
float2 d = abs(float2(length(p.xz), p.y)) - float2(r, h);
return min(max(d.x, d.y), 0) + length(max(d, 0));
}
float4x4 rotate(float theta) {
float c = cos(theta);
float s = sin(theta);
return mul(float4x4(
float4(c, 0, s, 0),
float4(0, 1, 0, 0),
float4(-s, 0, c, 0),
float4(0, 0, 0, 1)
), float4x4(
float4(1, 0, 0, 0),
float4(0, c, -s, 0),
float4(0, s, c, 0),
float4(0, 0, 0, 1)
));
}
float sceneSDF(float3 p) {
float t = _Time.y;
p = mul(rotate(t), p);
float cube = cubeSDF(p, 1);
float sphereA = sphereSDF(p, 1.3);
float cylinderA = cylinderSDF(p, 2, 0.6);
float cylinderB = cylinderSDF(float3(p.y, p.x, p.z), 2, 0.6);
float cylinderC = cylinderSDF(float3(p.x, p.z, p.y), 2, 0.6);
float dist = max(max(cube, sphereA), -min(min(cylinderA, cylinderB), cylinderC));
float l = 0.8;
float r = 0.4;
float sphereB = sphereSDF(p + float3(l, 0, 0), r);
float sphereC = sphereSDF(p + float3(-l, 0, 0), r);
float sphereD = sphereSDF(p + float3(0, l, 0), r);
float sphereE = sphereSDF(p + float3(0, -l, 0), r);
float sphereF = sphereSDF(p + float3(0, 0, l), r);
float sphereG = sphereSDF(p + float3(0, 0, -l), r);
dist = min(dist, min(min(min(sphereB, sphereC), min(sphereD, sphereE)), min(sphereF, sphereG)));
return dist;
}
float shortestDistanceToSurface(float3 eye, float3 marchingDirection, float start, float end) {
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sceneSDF(eye + depth * marchingDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
return depth;
}
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
return end;
}
}
return end;
}
float3 rayDirection(float fieldOfView, float2 size, float2 fragCoord) {
float2 xy = fragCoord - size * 0.5;
float z = size.y / tan(radians(fieldOfView) * 0.5);
return normalize(float3(xy, -z));
}
float3 estimateNormal(float3 p) {
return normalize(float3(
sceneSDF(float3(p.x + EPSILON, p.y, p.z)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x - EPSILON, p.y, p.z)),
sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y + EPSILON, p.z)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y - EPSILON, p.z)),
sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z + EPSILON)) - sceneSDF(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z - EPSILON))
));
}
float3 phongContribForLight(float3 k_d, float3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye, float3 lightPos, float3 lightIntensity) {
float3 N = estimateNormal(p);
float3 L = normalize(lightPos - p);
float3 V = normalize(eye - p);
float3 R = normalize(reflect(-L, N));
float dotLN = dot(L, N);
float dotRV = dot(R, V);
if (dotLN < 0.0) {
// Light not visible from this point on the surface
return float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
if (dotRV < 0.0) {
// Light reflection in opposite direction as viewer, apply only diffuse
// component
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN);
}
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN + k_s * pow(dotRV, alpha));
}
float3 phongIllumination(float3 k_a, float3 k_d, float3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye) {
float iTime = _Time.y;
const float3 ambientLight = 0.5 * float3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
float3 color = ambientLight * k_a;
float3 light1Pos = float3(4.0 * sin(iTime), 2.0, 4.0 * cos(iTime));
float3 light1Intensity = float3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye, light1Pos, light1Intensity);
float3 light2Pos = float3(2.0 * sin(0.37 * iTime), 2.0 * cos(0.37 * iTime), 2.0);
float3 light2Intensity = float3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye, light2Pos, light2Intensity);
return color;
}
float4x4 viewMatrix(float3 eye, float3 center, float3 up) {
// Based on gluLookAt man page
float3 f = normalize(center - eye);
float3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
float3 u = cross(s, f);
return float4x4(
float4(s, 0),
float4(u, 0),
float4(-f, 0),
float4(0, 0, 0, 1)
);
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target {
float3 viewDir = rayDirection(45, 1, i.uv);
float3 eye = float3(8, 5, 7);
float4x4 viewToWorld = viewMatrix(eye, 0, float3(0, 1, 0));
float3 worldDir = mul(float4(viewDir, 0), viewToWorld).xyz; // 这里需要反过来使用mul计算
float dist = shortestDistanceToSurface(eye, worldDir, MIN_DIST, MAX_DIST);
if (dist > MAX_DIST - EPSILON) {
// Didn't hit anything
return 0;
}
// The closest point on the surface to the eyepoint along the view ray
float3 p = eye + dist * worldDir;
float3 K_a = 0.05;
float3 K_d = abs(p); // float3(0.7, 0.2, 0.2);
float3 K_s = 1;
float shininess = 10.0;
float3 color = phongIllumination(K_a, K_d, K_s, shininess, p, eye);
return fixed4(color, 1);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
九、进阶:Unity后处理绘制3D效果,体积云等(todo…)
参考:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1964y157fA/
todo,留到另外的文章说明